
Blockchain wallets are an essential way to control digital currency. They can perform various functions, from ensuring safety and security to offering convenience. In this guide, you will learn about the different types of wallets, how they work, and how to find the best one for your needs. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the mechanics of digital asset wallets—where security, convenience, user experience, and technical barriers intersect.
A cryptocurrency wallet is a virtual wallet used to transact with digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and others. Unlike conventional wallets that hold physical money, crypto wallets don't store the actual currency. Instead, they securely store private keys—unique digital codes that grant you access to your cryptocurrencies on the blockchain, where all transactions are recorded.
There are a few ways to categorize blockchain wallets. The most straightforward difference is the following:
Hot wallets stay connected to the internet, which affords them a convenience that is extremely useful for executing transactions. When you want to send or receive cryptocurrency, you use a software application from your computer, smartphone, or web browser.
A cold wallet stores one's private keys offline and is, therefore, less prone to being hacked. It is perfect for storing keys for a longer period of time.
Another method of classifying wallets is based on who controls the private keys.
In this case, your private keys are held by someone else on your behalf. This is like the bank holding your money. You log in to your account on the exchange or service provider's platform, and they manage all the rest from a technical point of view. The downside is that you also transfer the trust of asset safety to the service provider. Examples: Coinbase, Binance, Kraken.
You are in total control of your private keys in a non-custodial wallet. When setting up a non-custodial wallet, you generate a private key only you know. You are responsible for maintaining this key safely and securely. Examples: MetaMask (Ethereum-based), Phantom (Solana-based), and Keplr (Cosmos-based).
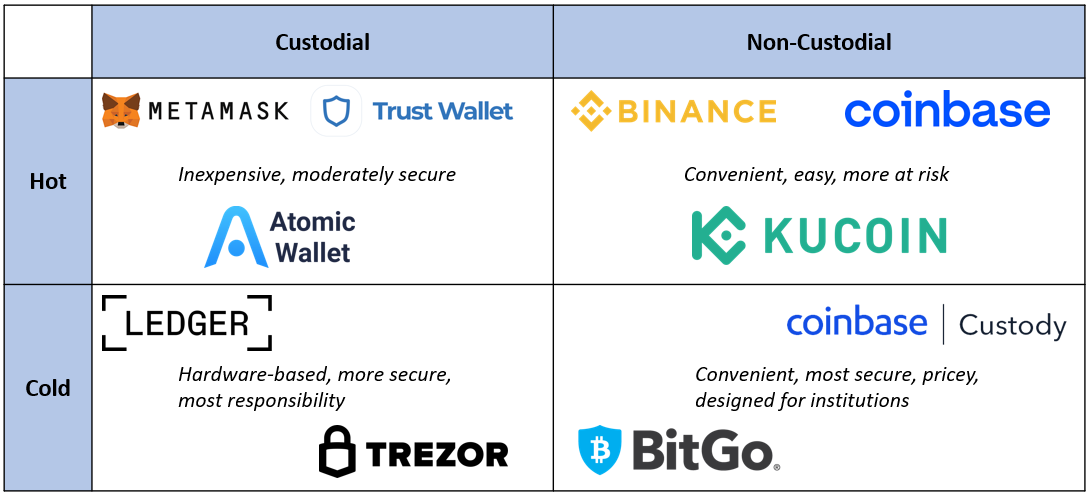
Figure 1. Hot vs Cold, Custodial vs Non-Custodial wallets
Cold wallets are more secure since they are kept offline. They are thus appropriate for holding crypto assets for an extended period. The following are three, more technical security features that can be applied to both hot and cold wallets:
MPC wallets use advanced cryptographic techniques to split your private key into multiple parts, each held by different parties. No single party can reconstruct the entire key or authorize transactions independently. Examples: Fireblocks, Cobo, Copper, Liminal, BitGo.
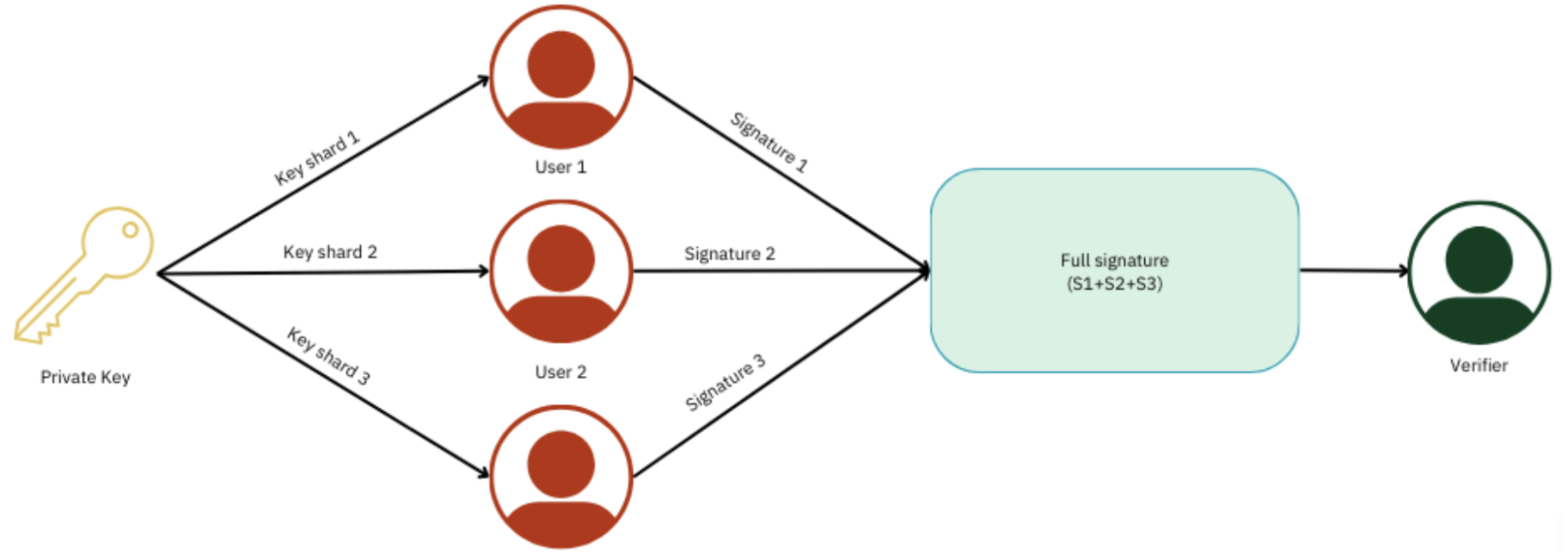
Fig.2. Multi-Party Computation (MPC) Wallets Diagram
Multi-Sig wallets require the signatures of all parties involved to validate a transaction. It is good practice when handling shared funds, as in the case of a company, which requires various stakeholders to authorize a transaction. Examples: BitGo, Safe Global (Gnosis Safe).
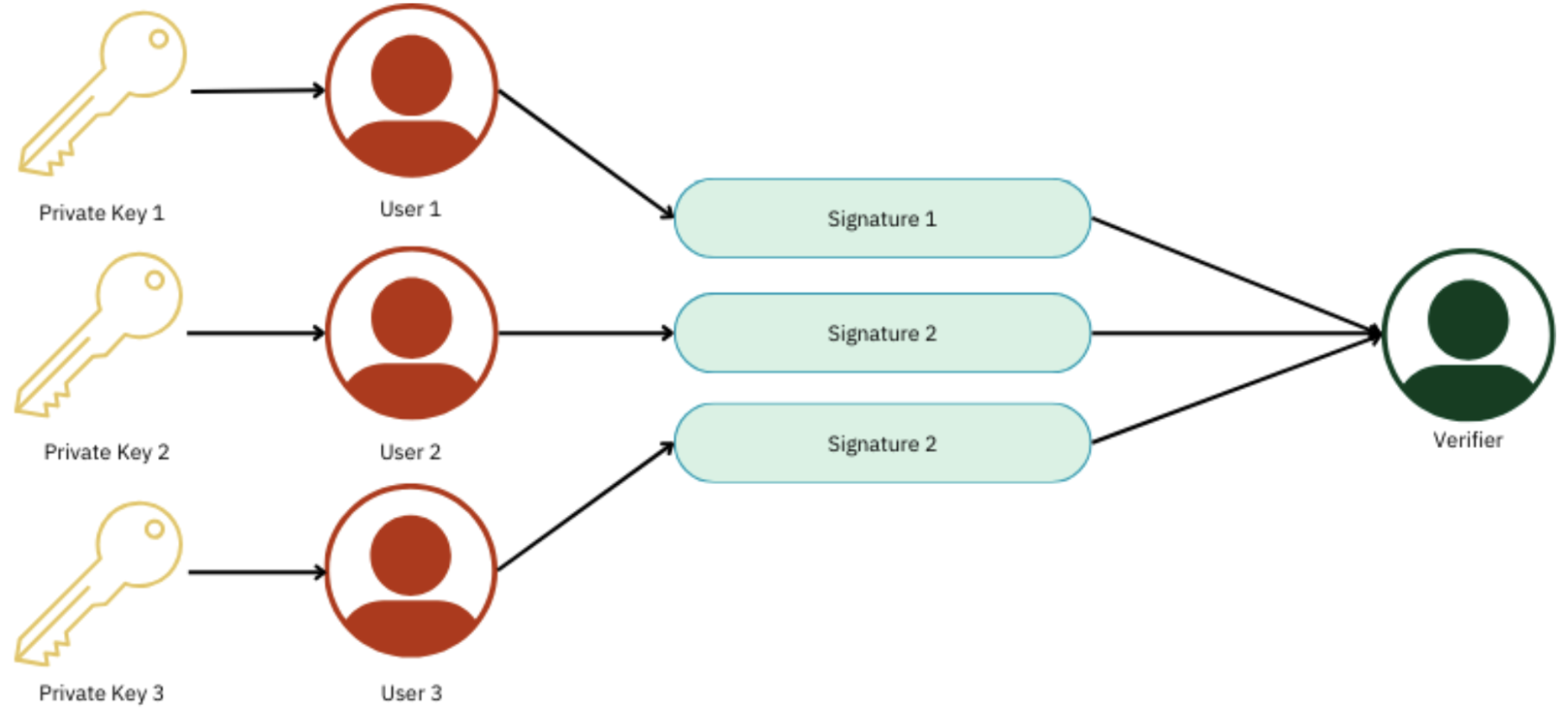
Fig.3. Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig) Wallets Diagram
HSMs are physical devices that manage digital keys and perform cryptographic operations. They provide a high level of security by isolating the keys in a secure environment, making unauthorized access extremely difficult. Examples: AWS CloudHSM, IBM Cloud HSM.
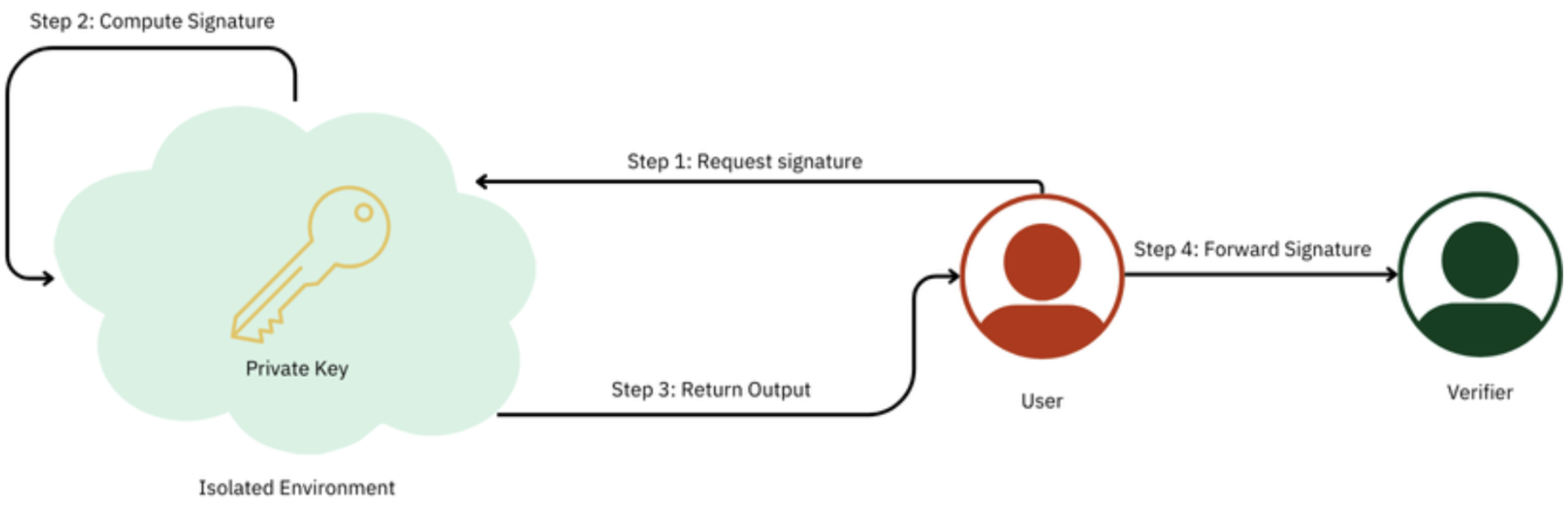
Fig.4. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) Diagram


Revolut partnered with Fireblocks to eliminate manual treasury operations and enhance their digital asset infrastructure. This integration enabled automated security, faster integration of new tokens and liquidity providers, and streamlined scaling with Fireblocks' MPC-CMP technology and API. Learn more about Revolut and Fireblocks.


Safe Global (former Gnosis Safe) is one of the most well-known Multi-Sig wallet companies, and it is used to ensure that all decisions are made with a group consensus. For example, a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) might have Safe Global as a layer for its treasury or NFT collection with multi-sig approval in place. Learn more about Siemens and their NFT collection, created to celebrate their 175th anniversary.



MetaMask is the most common non-custodial wallet that interacts with the Ethereum blockchain. Similarly, Phantom is Solana's most common wallet. They are particularly popular among crypto-native users engaging with decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).


Before selecting a wallet, consider the following:
What is the best wallet for beginners?
Hot wallets are best for beginners as they are user-friendly. Custodial wallets offer the added advantage of convenience.
How can I ensure the highest security for my assets?
Non-custodial cold wallets assure the highest security for individuals. Advanced features like MPC, Multi-Sig, and HSM can further enhance security.
What should organizations consider when choosing a wallet?
Multi-Sig wallets are popular for organizations and institutions due to collective decision-making. Adding MPC can enhance governance and security.
Can I combine different wallet features?
A combination of hot and cold wallets, supported by advanced security features such as MPC and Multi-Sig, gives a balanced approach to security, especially for institutions.
What are the risks of using a custodial wallet?
The critical risk to using a custodial wallet is trusting a third party to hold your private keys. If the third party is breached, so are your assets. Always go for well-known services and use additional security options like two-factor authentication.
How do I recover my funds if I lose my non-custodial wallet?
If you lose access to your non-custodial wallet, you can restore funds by using a seed phrase that should have been provided during the setup of the wallet. Make sure you keep this seed phrase very safe and don't expose it to anyone.
Are hardware wallets worth the investment?
Hardware wallets provide an added security layer by keeping private keys offline. It's especially worth it for long-term holders or people with large sums of cryptocurrency.
Investopedia: Cryptocurrency Wallets
CoinDesk: What is Crypto Custody
ZenGo: How MPC Wallets Work
Ledger: What is a Multi-Sig Wallet
Ledger: Hardware Security Module (HSM)
CoinTelegraph: Account Abstraction
In taking a closer look at the various blockchain wallets, we have noted the significance of having the types of wallets align with specific needs. From the convenience of hot wallets to the robust security of cold wallets, from a choice between custodial and non-custodial setups, there's something for everyone. This is just an introductory guide; the journey of managing cryptocurrencies has much more space to dig deeper, ask the right questions, and find the best solution for your needs.